increase your memory and Brain processing power in "just 3 months" with
whole brain thinking
In Just 03 Months,
Witness an increase in your ability to Score Good
Grades in Examinations

With Whole Brain Thinking, you will not need Tuitions
and will avoid ROTE Learning.
With Whole Brain Thinking, you will not need Tuitions
and will avoid ROTE Learning.
Within 01 Month,
You will witness
1. Improved Self-confidence
2. Emotional Maturity
3. Stress-free examinations
4. Stress-free learning
5. Longer Attention span
6. Enhanced Grasping
7. Increased Memory
8. Excellent recall capability
and More
Please fill this form,
We will call you right back
What is Neuro+Cognition?
Neuro: Neural Wiring in the Brain
Importance of Neuroplasticity
The human brain is a remarkable organ that is capable of adapting to changes and learning throughout one’s life. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to change and reorganize itself in response to new experiences and learning, while neurocognitive development refers to the processes by which the brain develops and matures over time. Both neuroplasticity and neurocognitive development are critical to our ability to learn, grow, and adapt to new challenges.
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to new experiences. This process occurs throughout our lives and is essential for learning, memory, and cognitive function. Neuroplasticity allows the brain to form new neural connections and strengthen existing ones in response to new information or experiences. For example, when we learn a new skill, such as playing an instrument or speaking a new language, the brain forms new neural connections that allow us to perform that skill more efficiently over time.
The ability of the brain to change and adapt through neuroplasticity has important implications for both cognitive function and mental health. Research has shown that people with higher levels of neuroplasticity tend to have better cognitive function, including better memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Additionally, neuroplasticity has been linked to improved mental health outcomes, including reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Neurocognitive development, on the other hand, refers to the processes by which the brain develops and matures over time. This process begins in infancy and continues throughout childhood and adolescence. During this time, the brain undergoes significant changes in structure and function, which are essential for the development of cognitive abilities such as language, reasoning, and problem-solving.
The importance of neurocognitive development cannot be overstated. The brain’s development during childhood and adolescence lays the foundation for cognitive function and mental health in adulthood. Early experiences and learning opportunities have a significant impact on brain development and can shape a child’s cognitive abilities and mental health outcomes for the rest of their lives.
The importance of both neuroplasticity and neurocognitive development underscores the need for lifelong learning and cognitive stimulation. It is essential to continue learning and challenging the brain throughout one’s life to maintain cognitive function and promote neuroplasticity. Activities such as learning a new skill, reading, or engaging in intellectually stimulating hobbies can help promote neuroplasticity and cognitive function.
In conclusion, neuroplasticity and neurocognitive development are critical to our ability to learn, grow, and adapt throughout our lives. These processes allow the brain to change and adapt in response to new experiences and learning opportunities, shaping our cognitive abilities and mental health outcomes over time. It is essential to continue learning and engaging in intellectually stimulating activities throughout our lives to promote neuroplasticity and cognitive function.
Cognition: Algorithms of the Mind
Why Learning has become Stressful?

In today’s world, learning has become an essential aspect of our lives. However, the process of learning has become increasingly stressful, and one of the primary reasons for this is the lack of neurocognitive development. Neurocognitive development refers to the development of cognitive abilities and neural structures that allow us to process information efficiently. The lack of neurocognitive development is affecting the way students learn, leading to stress and anxiety.
One of the main reasons for the lack of neurocognitive development is the overuse of technology. The use of electronic devices has become ubiquitous in our daily lives, and it has a significant impact on our cognitive development. The constant use of technology has been linked to a decrease in attention span, memory capacity, and cognitive flexibility. This can make it challenging for students to focus on their studies, leading to stress and anxiety.
Moreover, the lack of physical activity is also contributing to the lack of neurocognitive development. Physical activity has been shown to be essential for brain development, and it can have a positive impact on cognitive abilities such as attention, memory, and problem-solving. Unfortunately, many students are leading sedentary lifestyles, spending long hours sitting in front of screens, which can lead to a decrease in brain function.
The lack of neurocognitive development is not only affecting students’ academic performance but also their mental health. Stress and anxiety are prevalent among students today, and it can lead to a range of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety disorders. The pressure to perform well in school, coupled with the lack of neurocognitive development, can be overwhelming for students, leading to a decrease in mental well-being.
In conclusion, learning has become increasingly stressful due to the lack of neurocognitive development. The overuse of technology, lack of physical activity, and poor nutrition are all contributing factors. It is essential to address these issues to improve cognitive function and mental well-being among students. By promoting a healthy lifestyle that includes physical activity, a balanced diet, and limited screen time, we can help students develop the cognitive abilities they need to succeed in their academic and personal lives.
What is Whole Brain Thinking ?
A Well networked Brain with Enhanced Learning, Retention and Recall capabilities.
Left Brain : Analytical Center
The left hemisphere of the brain is primarily responsible for logical and analytical thinking, as well as verbal communication and language processing.
Right Brain : Creative Center
The Right hemisphere of the brain is primarily responsible for many cognitive functions, including creativity, intuition, and spatial awareness.
Importance of Whole Brain Thinking

Whole brain thinking refers to the idea of using both hemispheres of the brain together in a coordinated and integrated way. This approach has been linked to a number of benefits, which arise from the development of the neural connections that allow for this type of thinking.Here are some of the benefits of whole brain thinking due to neurocognitive development:
1. Increased creativity: The right hemisphere of the brain is often associated with creativity, while the left hemisphere is associated with logic and reasoning. By using both hemispheres together, individuals can tap into their full creative potential.
2. Improved problem-solving: Whole brain thinking enables individuals to approach problems from different angles and to consider multiple solutions. This can lead to more effective problem-solving and decision-making.
3. Better memory retention: Studies have shown that when information is processed in a more holistic manner, it is better retained in long-term memory. Whole brain thinking enables individuals to process information in a more integrated way, leading to better memory retention.
4. Enhanced learning: By engaging both hemispheres of the brain, whole brain thinking can lead to more effective learning. This is particularly true in areas that require both logical and creative thinking, such as science, math, and art.
5. Improved emotional regulation: The right hemisphere of the brain is involved in processing emotions, while the left hemisphere is involved in regulating them. By using both hemispheres together, individuals can improve their ability to regulate their emotions in a more balanced way.
Overall, the development of whole brain thinking can lead to a range of cognitive, emotional, and behavioural benefits that can enhance a person’s quality of life.
Benefits of
Whole Brain Thinking
- Age 17 to 24 Years

Higher Confidence levels
Improved Self-Confidence and self-Worth
Improved communication skills

One important aspect of neurocognitive development that contributes to improved communication skills is the development of language abilities. As the brain matures, individuals become more adept at using and understanding language, which can improve their ability to communicate with others. For example, as children grow and develop, they typically learn new vocabulary and grammar rules, which allow them to express themselves more clearly and effectively.
Another important aspect of neurocognitive development that can contribute to improved communication skills is the development of executive functioning skills. Executive functioning refers to the cognitive processes that enable individuals to plan, organize, initiate, monitor, and evaluate their own behavior. These skills are critical for effective communication, as they allow individuals to structure their thoughts, set goals, and monitor their own communication behaviors.
Finally, the development of social cognition can also contribute to improved communication skills. Social cognition refers to the ability to understand and interpret social cues, such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language. As individuals develop their social cognition, they become more skilled at interpreting these cues and adjusting their own communication behaviors accordingly. This can help them to better understand others and communicate more effectively with them.
Overall, neurocognitive development can have a significant impact on an individual’s communication skills, particularly with regard to language abilities, executive functioning skills, and social cognition. As the brain matures and grows, individuals become better equipped to communicate effectively with others, which can help them to build stronger relationships, succeed in academic and professional settings, and navigate the complex social world.

Champion's Mindset
Goal Oriented Thought processes with Actions
Numerical intelligence

Numerical intelligence, also known as mathematical intelligence, is the ability to reason, understand, and apply numerical concepts and operations. It involves the ability to think logically, analyze information, and solve problems using mathematical concepts and methods. This type of intelligence is important in many areas of life, including science, engineering, finance, and everyday decision-making.
Neurocognitive development plays a critical role in the development of numerical intelligence. The brain undergoes significant changes during childhood and adolescence that support the acquisition of mathematical skills and abilities. These changes include the development of the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions such as planning, attention, and working memory, and the parietal cortex, which is involved in spatial processing and number sense.
Research suggests that there are specific brain regions and neural networks that are involved in numerical processing. For example, the intraparietal sulcus (IPS) has been shown to be involved in number sense and basic arithmetic operations, while the prefrontal cortex is involved in more complex problem-solving and decision-making tasks.
In addition to neurocognitive development, environmental factors also play a role in the development of numerical intelligence.
Opportunities for math learning and practice, such as formal education and everyday activities that involve math, can have a significant impact on the development of mathematical abilities.
Overall, the development of numerical intelligence is a complex process that involves both neurocognitive and environmental factors. By understanding the role that these factors play in the development of mathematical abilities, we can better support the acquisition and refinement of these important skills.

Intuitive Intelligence
Heightened Intuitive ability of the Mind
Intuitive intelligence

Intuitive intelligence is a term that refers to the ability to understand complex concepts or situations quickly, without relying on conscious reasoning. It is often associated with creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making. Neurocognitive development plays an important role in the development of intuitive intelligence.
Neurocognitive development refers to the growth and maturation of the brain and nervous system, which occurs throughout childhood and adolescence. During this period, the brain undergoes significant changes that affect cognitive processes such as perception, attention, memory, language, and reasoning.
Research suggests that intuitive intelligence is related to the development of the prefrontal cortex, a region of the brain that is responsible for complex cognitive processes such as decision-making, planning, and working memory. Studies have found that individuals with well-developed prefrontal cortices are better able to make intuitive decisions based on their experiences and knowledge.
Moreover, the development of intuitive intelligence is also influenced by the development of the limbic system, which is involved in processing emotions and social interactions. This system helps individuals to perceive and interpret social cues and emotional information, which can inform intuitive decisions.
Overall, the development of intuitive intelligence is a complex process that is influenced by various factors, including neurocognitive development. As the brain matures, individuals become better able to make intuitive decisions based on their experiences and knowledge, which can be a valuable asset in many different contexts.

Enhanced Grasping
Avg. Increase in Grasping
70%
Enhanced Grasping

Neurocognitive development refers to the growth and changes that occur in the brain’s cognitive functions over time. It is the process through which individuals acquire the ability to reason, think, learn, and solve problems.
Enhanced understanding is one of the key outcomes of neurocognitive development. As the brain develops, individuals are better able to process information, organize their thoughts, and make connections between ideas. This leads to an increased ability to understand complex concepts and ideas.
For example, in early childhood, children may struggle to understand abstract concepts such as time, space, and cause and effect. However, as their brain develops, they become better able to understand these concepts and apply them to their everyday life.
Similarly, as individuals progress through adolescence and into adulthood, they become better able to understand complex social and emotional situations. This is because their brain has developed the ability to process and integrate multiple sources of information, such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language.
Overall, neurocognitive development plays a critical role in enhancing our understanding of the world around us, and in shaping our ability to think, reason, and problem-solve.

Longer Attention span
Enhanced Attention Span
85%
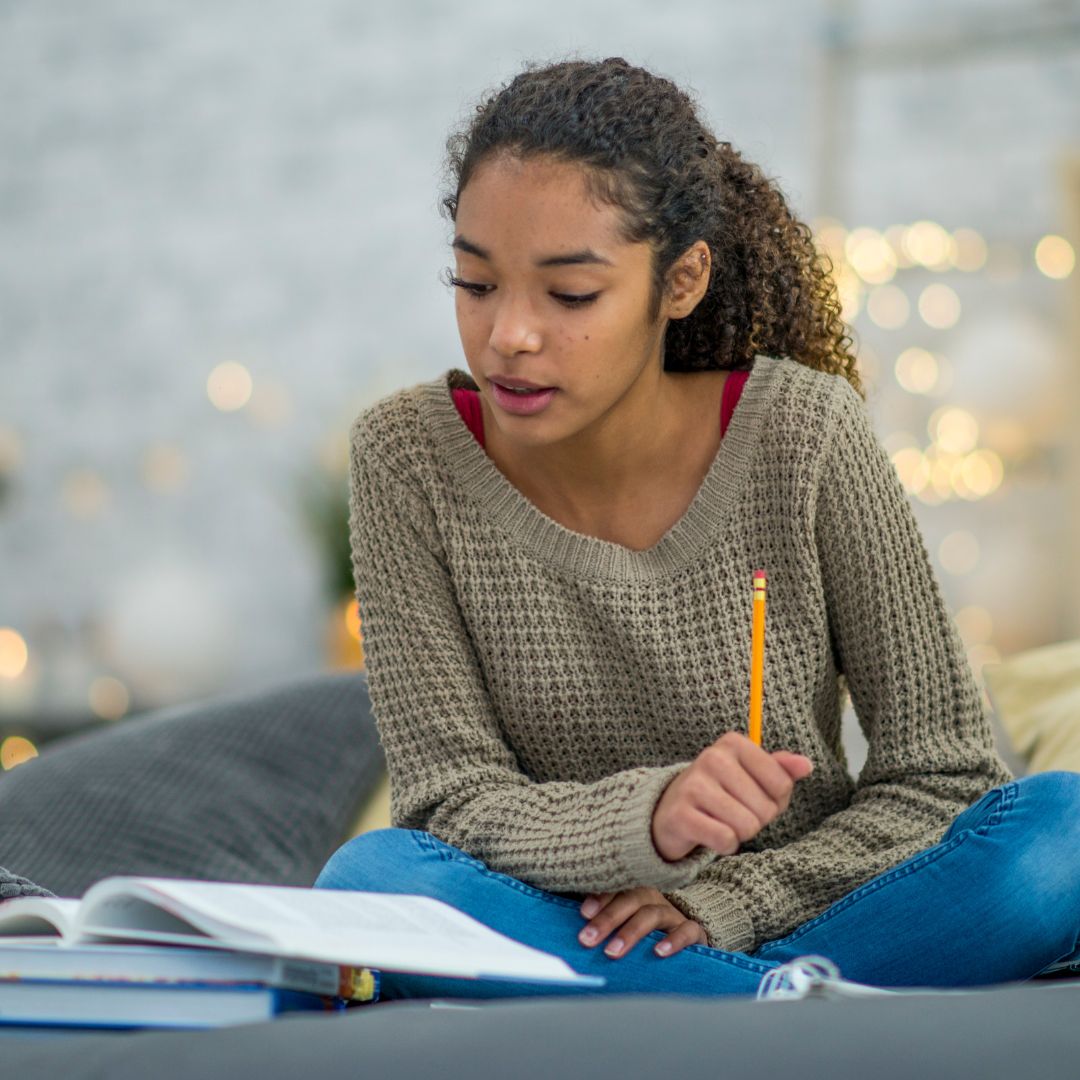
Longer Attention span

Attention span refers to the amount of time an individual can focus their attention on a particular task or stimulus. Neurocognitive development plays a significant role in the development of attention span, particularly in childhood and adolescence.
As children grow and develop, their attention span tends to increase. This is due to changes in their brain structure and function, such as increased myelination of neural pathways and the development of prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for higher-order cognitive processes such as attention and decision-making.
During adolescence, there is a significant increase in the ability to sustain attention and inhibit distractions. This is due to the ongoing development of prefrontal cortex and other brain regions involved in attention regulation. However, this increase in attention span may also be influenced by other factors, such as changes in motivation and interest in tasks.
It is important to note that attention span can still vary significantly among individuals, even within the same age group. Factors such as genetics, environmental influences, and individual differences in brain structure and function can all contribute to individual differences in attention span.
Overall, while neurocognitive development plays a significant role in the development of attention span, there are also many other factors that can influence an individual’s ability to sustain attention.

Clarity of Thought
Avg. improvement in Clarity
50%
Clarity of thought

Clarity of thought refers to the ability to think in a precise and focused way, free from confusion or ambiguity. It is closely related to cognitive processes such as attention, memory, and reasoning, which are all affected by neurocognitive development.
In early childhood, the brain undergoes rapid growth and development, which lays the foundation for later cognitive abilities. During this time, children acquire basic cognitive skills such as perception, attention, memory, and language, which are essential for clear thinking.
As children grow and mature, their cognitive abilities become more sophisticated, and they develop higher-level thinking skills such as abstract reasoning, critical thinking, and problem-solving. These skills are crucial for clarity of thought, as they allow individuals to analyze complex information, draw logical conclusions, and communicate their ideas effectively.
However, neurocognitive development is not limited to childhood, and the brain continues to develop throughout adulthood. Engaging in activities that promote cognitive function, such as learning a new language or playing brain games, can help to improve clarity of thought and enhance overall cognitive abilities.
In summary, neurocognitive development plays a vital role in the development of clarity of thought. By improving cognitive processes such as attention, memory, and reasoning, individuals can think more clearly, solve problems more effectively, and communicate their ideas more clearly.

Communication Skills
Improved Communication Skills
Improved communication skills

One important aspect of neurocognitive development that contributes to improved communication skills is the development of language abilities. As the brain matures, individuals become more adept at using and understanding language, which can improve their ability to communicate with others. For example, as children grow and develop, they typically learn new vocabulary and grammar rules, which allow them to express themselves more clearly and effectively.
Another important aspect of neurocognitive development that can contribute to improved communication skills is the development of executive functioning skills. Executive functioning refers to the cognitive processes that enable individuals to plan, organize, initiate, monitor, and evaluate their own behavior. These skills are critical for effective communication, as they allow individuals to structure their thoughts, set goals, and monitor their own communication behaviors.
Finally, the development of social cognition can also contribute to improved communication skills. Social cognition refers to the ability to understand and interpret social cues, such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language. As individuals develop their social cognition, they become more skilled at interpreting these cues and adjusting their own communication behaviors accordingly. This can help them to better understand others and communicate more effectively with them.
Overall, neurocognitive development can have a significant impact on an individual’s communication skills, particularly with regard to language abilities, executive functioning skills, and social cognition. As the brain matures and grows, individuals become better equipped to communicate effectively with others, which can help them to build stronger relationships, succeed in academic and professional settings, and navigate the complex social world.
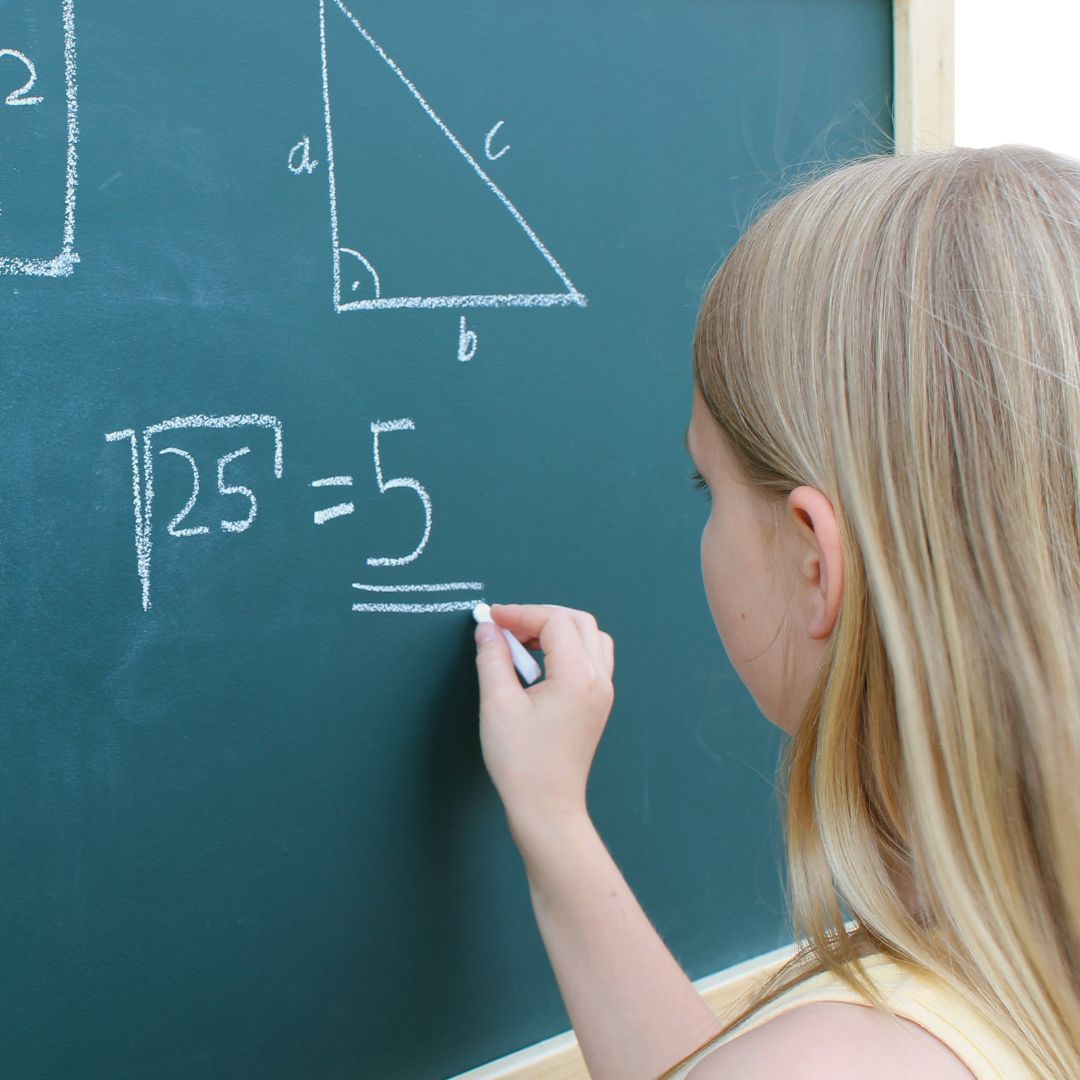
Numerical Intelligence
Enhanced Numerical Intelligence
Numerical intelligence

Numerical intelligence, also known as mathematical intelligence, is the ability to reason, understand, and apply numerical concepts and operations. It involves the ability to think logically, analyze information, and solve problems using mathematical concepts and methods. This type of intelligence is important in many areas of life, including science, engineering, finance, and everyday decision-making.
Neurocognitive development plays a critical role in the development of numerical intelligence. The brain undergoes significant changes during childhood and adolescence that support the acquisition of mathematical skills and abilities. These changes include the development of the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions such as planning, attention, and working memory, and the parietal cortex, which is involved in spatial processing and number sense.
Research suggests that there are specific brain regions and neural networks that are involved in numerical processing. For example, the intraparietal sulcus (IPS) has been shown to be involved in number sense and basic arithmetic operations, while the prefrontal cortex is involved in more complex problem-solving and decision-making tasks.
In addition to neurocognitive development, environmental factors also play a role in the development of numerical intelligence.
Opportunities for math learning and practice, such as formal education and everyday activities that involve math, can have a significant impact on the development of mathematical abilities.
Overall, the development of numerical intelligence is a complex process that involves both neurocognitive and environmental factors. By understanding the role that these factors play in the development of mathematical abilities, we can better support the acquisition and refinement of these important skills.
and more ....
Negative Impacts of
Rote Learning
Lack of Deep Understanding
Rote learning focuses on memorizing facts without fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Students may be able to regurgitate information without truly comprehending its meaning or application. This limits their ability to think critically, problem-solve, and apply knowledge in real-life situations.
Limited Learning Retention
Since rote learning primarily relies on repetition and memorization, the retention of information tends to be short-term. Students may forget the material shortly after the exam or assignment is completed, making it less effective for long-term learning and mastery.
Mental Inflexibility
Rote learning tends to promote rigid thinking patterns and inflexible knowledge. It does not encourage creativity, independent thinking, or the ability to connect and synthesize information from different sources. This can hinder students' ability to adapt to new situations, solve complex problems, or think critically.
Higher Emotional Stress
Rote learning can create a stressful learning environment, as students may feel pressure to memorize large amounts of information within a specific timeframe. This pressure can lead to anxiety, rote memorization without true understanding, and a negative association with learning in general.
Reduced Motivation and Exciting
Rote learning can be monotonous and repetitive, leading to reduced student motivation and engagement. When students are not actively involved in the learning process or do not see the relevance of the material to their lives, they may become disinterested, disengaged, and less inclined to pursue further education.
Reduced of higher-order skills
Rote learning tends to prioritize the memorization of facts and figures over the development of higher-order thinking skills such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. These skills are crucial for higher education and professional success, as they enable individuals to think critically, make connections, and solve complex problems.
Limited application to real-life situations
Rote learning often focuses on isolated facts or procedures without providing a broader context or real-life application. Students may struggle to apply their knowledge to real-world situations or understand the relevance and practicality of what they have learned.
Sukshma Dhrashta is a scientifically proven Program with FMRI Results
FMRI Results of Supramental Meditations
There have been several studies that have used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to investigate the effects of Supramental Meditations on brain activity. Here is one example of our findings:
# Default mode network: One consistent finding across many studies is that meditation appears to alter activity in the brain’s default mode network (DMN), which is a network of brain regions that are active when the brain is at rest and not focused on the outside world. During meditation, activity in the DMN tends to decrease, suggesting that meditation may quiet the “monkey mind” and help people focus their attention.
# Prefrontal cortex: Another consistent finding is that meditation appears to increase activity in the prefrontal cortex, which is the part of the brain responsible for executive functions like attention, decision-making, and working memory. This suggests that meditation may improve cognitive control and enhance the ability to regulate one’s thoughts and emotions.
# Insula: The insula is a brain region that is involved in self-awareness and introspection (the ability to sense the body’s internal state). Some studies have found that meditation can increase activity in the insula, suggesting that meditation may increase one’s ability to tune into bodily sensations and become more aware of their thoughts and emotions.
# Hippocampus: The hippocampus is a brain region that is important for memory and learning. Some studies have found that meditation can increase activity in the hippocampus, suggesting that meditation may improve memory and learning.
Overall, these findings suggest that Supramental Meditation can have a significant impact on brain activity and may lead to improvements in attention, emotion regulation, and cognitive control. However, it’s important to note that there is still much that is not fully understood about the neural mechanisms underlying meditation, and more research is needed to fully understand its effects on the brain.
Testimonials

Divyam Singal
My intuition has improved, and I am able to come up with ideas much more quickly. I am physically fitter and more athletic from what I used to be before the program. I feel Emotional and mental Stability throughout the day, specially during examinations.

Aum Vyas
Now, I don’t fear speaking on the Stage.

Akshaya Ramakrishnan
The program has helped me improve my communication skills and be more open to others. I am able to interact with others more easily. Academically, I don’t need to study a lot, just a read through the book is enough to help me remember the key concepts.
